 Distortion occurs due to the relief of locked-in stresses within a steel section or fabrication. At room temperature, the steel is sufficiently strong to accommodate such stresses, but at the galvanizing bath temperature (about 450°C), the steel`s yield strength may be reduced by up to 40% (Note, the steel recovers its full strength when it cools to ambient temperature).
Distortion occurs due to the relief of locked-in stresses within a steel section or fabrication. At room temperature, the steel is sufficiently strong to accommodate such stresses, but at the galvanizing bath temperature (about 450°C), the steel`s yield strength may be reduced by up to 40% (Note, the steel recovers its full strength when it cools to ambient temperature).
If the internal stresses, then exceed the steel`s yield strength the steel may distort due to plastic deformation. The occurrence of distortion is dependent upon the level and distribution of these internal stresses.
Stresses may be present for a variety of reasons which include:
- Variable steel section thicknesses forming the assembly
- The introduction of stresses due to welding
- Cold forming or bending the item
Given that the causes can be identified, it is possible to take precautions which should significantly reduce the potential for distortion:
- Use of hot rolled sections rather than cold rolled or cold formed sections where possible as these sections will have inherently lower internal stresses
- Maintain as uniform a steel section thickness as is practically possible so as to avoid the introduction of thermal stresses and issues with differential thermal expansion and contraction during the cycle of the galvanizing process. Ideally section thicknesses should not vary by a ratio of more than 2.5:1
- Prior to welding, a fabrication should not be jigged excessively tightly as this may lead to increased internal stresses
- Avoid over-welding – the welds should be no larger than what is essential to maintain the structural integrity of the fabricated component
- Welding should be a symmetrical as possible in order to ensure the stresses are balanced. This can be done by placing welds near the neutral axis or by balancing them around the axis
- Use a planned welding sequence to avoid an asymmetrical build-up of stresses
- Try to ensure that the article has as symmetrical a design as is practically possible. Asymmetric designs are more likely to result in unbalanced stresses which may result in distortion
- Where there is particular concern about distortion of large articles, consideration might be given to ensuring that it is single dipped. Double dipping while perfectly acceptable will introduce some level of thermal stresses which might contribute towards potential distortion
- Where an article cannot be single dipped due to its size consider splicing the structure so that it can be dipped as two separate parts, each being single dipped. The pieces may then be joined by bolting or welding after galvanizing.
- In the event that theses precautions cannot be implemented, consideration might be given to stress relieving an article prior to hot dip galvanizing.
Stress relieving may be carried out by controlled heating and cooling or by using the VSR (Vibratory Stress Relieving). If you wish to know more about this, there is an excellent article published by the South African Institute of Steel Construction (SAISC)
https://www.saisc.co.za/a-study-into-the-effects-of-residual-stresses-and-the-hot-dip-galvanizing-process/
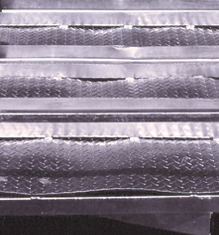 Where thin sheet or mesh is welded into a frame it is very likely that it will distort by buckling or bowing during the galvanizing process. The potential for distortion may be significantly reduced by galvanizing the frame separate to the sheet or mesh and then joining after galvanizing. Thin sheet has a relatively low rigidity and may also contain high internal stresses due to having been cold rolled. Increased rigidity might be achieved by folding over the edges of the sheet so reducing the potential for distortion. Alternatively, temporary bracing may be used to contain the work.
Where thin sheet or mesh is welded into a frame it is very likely that it will distort by buckling or bowing during the galvanizing process. The potential for distortion may be significantly reduced by galvanizing the frame separate to the sheet or mesh and then joining after galvanizing. Thin sheet has a relatively low rigidity and may also contain high internal stresses due to having been cold rolled. Increased rigidity might be achieved by folding over the edges of the sheet so reducing the potential for distortion. Alternatively, temporary bracing may be used to contain the work.
Ensure that consideration is given to good design for galvanizing. For example, provision of well-positioned vent holes of the correct size will enable the galvanizer to immerse work as rapidly as is practically possible so minimizing the introduction of potential thermal stresses.
